How much protein does a single egg contain, and why does it matter?
Dietary protein is essential for various bodily functions, from building and repairing tissues to supporting immune function. A single egg boasts a substantial amount of high-quality protein, making it a valuable component of a balanced diet. This protein is readily digestible and contains all nine essential amino acids. For example, a large egg typically provides approximately 6 grams of protein.
Eggs' protein content makes them a popular choice for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking to increase their protein intake. This protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair, crucial for maintaining healthy weight, and contributes to satiety, potentially aiding in weight management. The protein in eggs is well-absorbed by the body, unlike some plant-based protein sources. Furthermore, eggs offer various other essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, contributing to overall nutritional well-being. Historically, eggs have been a cornerstone of many cuisines worldwide, often playing a significant role in daily diets.
Read also:Amazing Jackie Evancho Americas Got Talents Singing Prodigy
Further exploration of egg nutrition will delve into the protein's role in specific diets, its impact on health markers, and cooking methods to optimize the utilization of this valuable nutrient.
Egg Protein Content
Understanding egg protein content is vital for appreciating its nutritional value. Protein quality, quantity, digestibility, and broader nutritional profile all contribute to the egg's overall benefit for health and wellness.
- Protein quantity
- Amino acid profile
- Digestibility
- Nutritional density
- Dietary inclusion
- Health benefits
Egg protein quantity is substantial, a significant source of dietary protein. The complete amino acid profile of egg protein makes it highly bioavailable. High digestibility contributes to efficient assimilation of the protein. Egg's nutritional density extends beyond protein, encompassing vitamins and minerals. Dietary inclusion of eggs is versatile, from breakfast to entrees. Health benefits related to protein intake include muscle repair and growth, and general maintenance of body tissue. These factors highlight the egg's importance as a nutritious food source, offering a complete and readily available protein source.
1. Protein Quantity
Quantifying protein is crucial for understanding the nutritional contribution of eggs. The amount of protein present in eggs directly influences its role in various dietary contexts. Factors impacting the protein content within an egg include its size, and potential variations due to breed and feeding practices. Understanding the relationship between protein quantity and egg consumption is essential for dietary planning and health management.
- Influence of Egg Size on Protein Content
Larger eggs generally contain more protein than smaller ones. This relationship holds true across various species and breeds. Variability in egg size, and thus protein content, requires consideration during dietary calculations.
- Protein Content in Relation to Egg Nutritional Density
The protein component within an egg contributes significantly to its overall nutritional value. Egg protein is recognized for its high biological value, meaning the body efficiently utilizes it. Alongside the protein content are other vital nutrients such as vitamins and minerals. A comparison of protein content relative to other food sources clarifies the nutritional value proposition of eggs.
Read also:
- Stylish Long Face Hairstyles For Men Enhance Your Look
- Protein Quantity in Different Dietary Contexts
Recognizing the protein content in an egg helps in various dietary situations. For athletes aiming for muscle growth and repair, the protein in eggs offers a readily available source. Individuals adhering to specific dietary regimens often incorporate protein-rich foods, such as eggs, into their meals. The quantity of protein influences dietary strategies and contributes to broader nutritional goals.
- Impact of Production Practices on Protein Content
Factors such as feeding regimens and the breed of the hen can influence the composition, including protein content, of eggs. Variations in these aspects can affect the protein levels, which can be important to note in dietary analysis and the selection of egg sources.
In summary, the protein quantity in eggs is a critical aspect of their nutritional profile. Understanding the variations in protein content, due to factors like egg size and production practices, is crucial for proper dietary planning and informed choices. The inclusion of eggs, given their protein profile, can be a significant part of balanced diets designed to support specific health goals or requirements.
2. Amino Acid Profile
The amino acid profile of egg protein is a critical determinant of its nutritional value. Eggs contain all nine essential amino acids, the building blocks of protein that the body cannot produce on its own. This complete amino acid profile is a key component of egg protein content, ensuring the body can efficiently utilize the protein for various functions, including tissue repair, muscle growth, and hormone production. The balanced distribution of essential amino acids in eggs makes them a valuable dietary source, particularly for individuals with specific dietary needs or heightened protein requirements.
The presence of all essential amino acids in adequate amounts is crucial for protein synthesis. Inadequate intake of even one essential amino acid can limit the body's ability to synthesize proteins efficiently. In contrast, the complete amino acid profile of egg protein enables optimal protein utilization. Furthermore, the quality of egg protein, as determined by its amino acid composition, often surpasses that of plant-based proteins, which may lack certain essential amino acids or have lower bioavailability. This superior amino acid profile makes eggs a preferred choice for individuals aiming for optimal protein intake and utilization, particularly athletes and those in periods of growth or recovery. Examples include use in dietary supplementation, and incorporation into meals to support building and repairing muscle tissues.
Understanding the precise amino acid composition within egg protein is essential for dietary planning and potentially for developing tailored nutritional strategies. The availability of high-quality protein, with an adequate balance of essential amino acids, contributes directly to various aspects of health and wellness. This understanding underpins the nutritional value proposition of eggs, establishing their significance in supporting a wide range of health goals and needs. For instance, the consistent intake of proteins with comprehensive amino acid profiles helps individuals achieve and maintain optimal body composition and function, contributing to a higher quality of life.
3. Digestibility
The digestibility of egg protein is a significant factor contributing to its nutritional value. High digestibility means the body efficiently breaks down and absorbs the protein, maximizing its utilization for various bodily functions. This efficient absorption contrasts with proteins from certain plant sources that may be less digestible. The superior digestibility of egg protein arises from its unique amino acid composition and specific protein structures. Factors influencing digestibility include the form in which the protein is consumed (e.g., whole egg, egg white, or egg yolk), preparation methods, and individual physiological factors. These factors play a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of the protein's assimilation by the body.
The high digestibility of egg protein has practical implications for various populations. For individuals with digestive sensitivities or compromised digestive function, the ease with which egg protein is processed can be advantageous. For athletes and bodybuilders seeking rapid muscle protein synthesis, the quick absorption characteristic of egg protein is a beneficial feature. Likewise, the digestibility of egg protein allows for its relatively straightforward incorporation into a wide range of diets and meal preparations. This ease of integration and assimilation into the body's systems is crucial to daily nutritional strategies, particularly for people with varied dietary needs. Furthermore, the high bioavailability of egg protein, a direct result of its digestibility, facilitates the swift utilization of its amino acids for various biological processes. The efficient breakdown and absorption of egg protein ensure an optimal contribution to tissue repair, growth, and other vital bodily functions.
In conclusion, the digestibility of egg protein is a key attribute enhancing its nutritional value. High digestibility translates to efficient absorption and utilization, impacting diverse populations and dietary strategies. This characteristic underscores the protein's importance as a valuable component of a balanced diet, particularly in contexts requiring optimal protein assimilation. Further research into specific factors influencing digestibility could lead to strategies for enhancing the effectiveness of egg protein in various dietary settings.
4. Nutritional Density
Nutritional density describes the abundance of essential nutrients relative to the calorie content of a food. Eggs, with their protein content, exemplify this concept. Understanding this relationship is crucial for evaluating the true nutritional value of eggs in a balanced diet. Nutritional density, in conjunction with protein content, informs choices regarding dietary strategies and overall health management.
- Macro-Nutrient Concentration
Eggs exhibit a high concentration of essential macro-nutrients like protein, alongside modest amounts of healthy fats and carbohydrates. This nutrient profile, when considered in relation to their relatively low calorie count, highlights their nutritional density. The significant protein content within eggs, coupled with the presence of other macro-nutrients, allows for adequate energy provision while contributing to satiety and promoting various bodily functions.
- Micronutrient Profile
Beyond macro-nutrients, eggs are a source of essential vitamins and minerals. This combination of micronutrients, in conjunction with high protein content, places eggs in a favorable position within the context of balanced nutrition. The presence of crucial micronutrients, such as choline and various B vitamins, further strengthens the overall nutritional density of eggs, impacting various physiological processes.
- Bioavailability of Nutrients
The bioavailability of nutrients, essentially how efficiently the body absorbs and utilizes them, is enhanced in eggs. This high bioavailability, combined with the considerable protein content, underscores the nutritional density of egg consumption in supporting various bodily functions. Eggs offer readily absorbable nutrients, enabling efficient utilization of the included protein and other essential components.
- Comparative Nutritional Density
Comparing eggs to other calorie-dense foods reveals a favorable profile for nutritional density. The relative abundance of essential nutrients per calorie in eggs illustrates their value in various dietary contexts. This comparison showcases the nutritional efficiency of eggs, making them a compelling choice for maintaining overall health and well-being, especially in conjunction with balanced diets.
In conclusion, the nutritional density of eggs, arising from their high protein content, diverse nutrient profile, and efficient nutrient bioavailability, underscores their significance in dietary planning and health maintenance. The density of nutrients within eggs, relative to their calorie count, contributes to a balanced diet and supports various aspects of optimal well-being. These features make eggs a valuable food source for a variety of dietary requirements and health goals.
5. Dietary Inclusion
Dietary inclusion of eggs, given their protein content, is a critical aspect of nutritional planning. The incorporation of eggs into diverse dietary regimens impacts overall protein intake and nutrient balance. Strategic inclusion of eggs considers individual dietary needs and preferences, alongside health goals. Real-world examples of successful dietary inclusion demonstrate the positive impact of egg consumption on health outcomes, particularly when coupled with a balanced diet. This integration requires careful consideration of portion sizes and frequency to maintain nutritional equilibrium.
Practical applications of this understanding include creating meal plans tailored to specific dietary requirements, whether for athletes, individuals seeking weight management, or those with particular nutritional needs. The protein in eggs can be incorporated into a variety of dishes, from breakfast meals to main courses, optimizing protein intake within the overall dietary strategy. For instance, utilizing eggs in omelets, scrambles, or as a component of protein-rich salads facilitates balanced meal preparation. Furthermore, understanding the protein content enables individuals to make informed choices about egg consumption, aligning their dietary habits with desired health outcomes. Adjustments in portion sizes and frequency of egg consumption ensure that dietary inclusion aligns with individual nutritional goals. The inclusion of eggs needs to be strategic, factoring into the broader nutritional approach.
In summary, the dietary inclusion of eggs, considering their significant protein content, plays a key role in achieving and maintaining a balanced diet. Effective integration into dietary plans hinges on a comprehensive understanding of individual needs, including protein requirements and overall health goals. This understanding empowers individuals to make informed choices and design dietary regimens that effectively leverage the benefits of egg consumption for optimal well-being. Challenges in dietary inclusion, such as potential allergies or intolerances, necessitate careful consideration and adjusted strategies. Consequently, mindful and strategic dietary inclusion of eggs, factored within the broader dietary context, contributes to well-rounded nutritional practices and positive health outcomes.
6. Health Benefits
The protein content in eggs is intricately linked to a multitude of health benefits. This essential nutrient, readily available in eggs, plays a crucial role in supporting various bodily functions, influencing overall health and well-being. The following exploration examines key facets of these benefits, emphasizing the contribution of egg protein.
- Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein, a cornerstone of muscle tissue, is crucial for growth and repair. Eggs, rich in high-quality protein, provide essential amino acids necessary for these processes. This is particularly relevant for athletes, individuals recovering from injury, or those focused on maintaining muscle mass. Adequate protein intake, often supplemented by eggs, supports these physiological processes, contributing to improved physical performance and overall fitness.
- Maintaining Healthy Weight
The protein content in eggs promotes satiety, potentially contributing to reduced overall calorie intake. This effect arises from the protein's ability to promote feelings of fullness, decreasing the likelihood of overeating. This aspect is pertinent to individuals aiming to maintain or achieve a healthy weight, as the impact on appetite regulation can positively influence dietary choices.
- Boosting Immunity
Essential amino acids, plentiful in egg protein, are fundamental components of antibodies and other immune system proteins. Adequate protein intake, including from eggs, supports the overall function of the immune system, potentially enhancing the body's ability to defend against illness and infection. This role of egg protein is particularly relevant in maintaining a robust immune response.
- Improving Brain Function
Choline, a nutrient present in eggs, plays a significant role in brain development and function. Adequate choline intake, often associated with egg consumption, supports cognitive functions, memory, and overall brain health. Eggs, through their high choline content, provide essential support for neurotransmitter production and transmission, impacting brain health.
In conclusion, the protein content in eggs, acting as a foundational building block for various bodily functions, contributes significantly to overall health. The multifaceted benefits outlinedfrom muscle maintenance to brain function, and immune supporthighlight the value of incorporating eggs into a balanced diet. The high-quality protein and diverse nutrient profile in eggs effectively support health and well-being across different stages of life and specific health goals.
Frequently Asked Questions about Egg Protein Content
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the protein content of eggs and its nutritional implications. Accurate information is provided to clarify misconceptions and promote informed dietary choices.
Question 1: How much protein is in a single egg?
A single large egg typically contains approximately 6 grams of protein. Variations in egg size can influence the exact amount, so consulting reliable nutritional databases for specific measurements is recommended.
Question 2: Is egg protein of high quality?
Egg protein is considered high-quality due to its complete amino acid profile. This means it contains all the essential amino acids the body requires. This characteristic makes egg protein highly bioavailable and effective for various bodily functions.
Question 3: How digestible is egg protein?
Egg protein is highly digestible. The body efficiently breaks down and absorbs the protein, maximizing its utilization for bodily processes. Compared to some plant-based protein sources, egg protein demonstrates superior digestibility.
Question 4: Does egg protein content vary based on preparation methods?
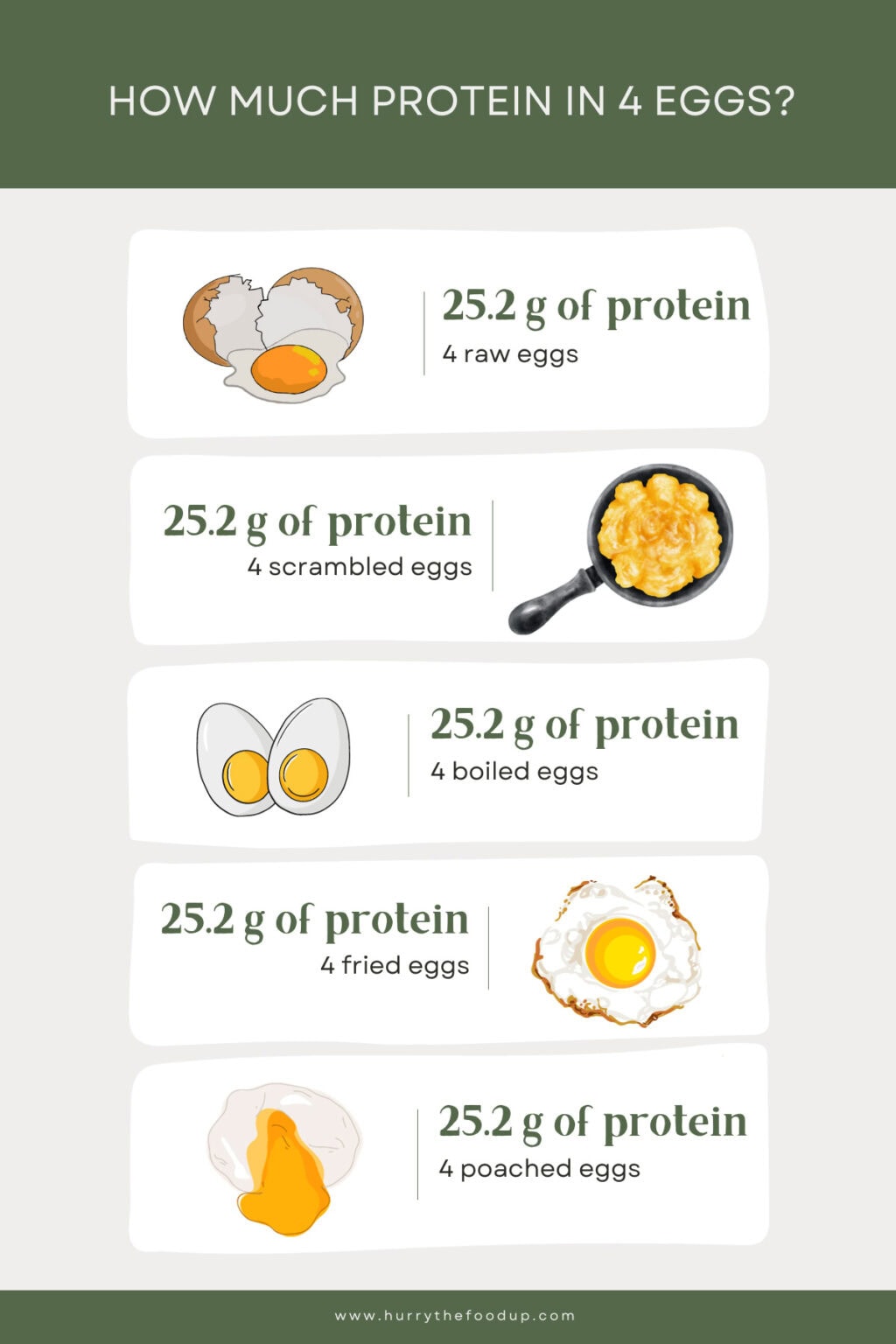
The protein content of eggs remains relatively consistent regardless of common preparation methods. Cooking techniques, such as frying or boiling, do not significantly alter the overall protein quantity. Variations in overall nutritional density may occur due to other components in a dish, not egg protein itself.
Question 5: Are there any potential drawbacks to consuming eggs due to their protein content?
While eggs are a valuable protein source, individuals with specific dietary needs or sensitivities should consult with healthcare professionals. Potential concerns might include cholesterol levels in some individuals or allergies to eggs themselves. A balanced diet that considers individual needs is crucial.
In summary, the protein content of eggs makes them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. The high quality and digestibility of egg protein contribute to its efficacy in various nutritional contexts. However, individual needs and sensitivities should be considered when incorporating eggs into a diet.
Further exploration into egg nutritional components and their impact on specific health goals might be beneficial.
Conclusion
This exploration of egg protein content reveals a nutrient of significant importance within a balanced diet. The high quantity of high-quality protein, coupled with a complete amino acid profile and exceptional digestibility, positions eggs as a valuable dietary component. Factors influencing protein content, such as egg size and production methods, merit consideration for personalized dietary strategies. The nutritional density of eggs extends beyond protein, encompassing essential vitamins and minerals, further enriching their contribution to overall health. Strategic inclusion of eggs, considering individual needs and preferences, facilitates optimal nutritional intake and supports various health goals. The multifaceted benefits, encompassing muscle growth and repair, weight management, and immune function, underscore the importance of eggs in various dietary contexts.
In light of the comprehensive examination of egg protein content, the focus should shift towards the nuanced application of this knowledge. Future dietary considerations should prioritize the integration of this nutrient within well-structured meal plans, taking into account individual sensitivities and needs. Further research into the long-term effects of consistent egg consumption within diverse dietary patterns can provide more comprehensive insights, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of dietary approaches centered around eggs.
Article Recommendations